- Docs Home
- About TiDB
- Quick Start
- Develop
- Overview
- Quick Start
- Build a TiDB Cluster in TiDB Cloud (Developer Tier)
- CRUD SQL in TiDB
- Build a Simple CRUD App with TiDB
- Example Applications
- Connect to TiDB
- Design Database Schema
- Write Data
- Read Data
- Transaction
- Optimize
- Troubleshoot
- Reference
- Cloud Native Development Environment
- Third-party Support
- Deploy
- Software and Hardware Requirements
- Environment Configuration Checklist
- Plan Cluster Topology
- Install and Start
- Verify Cluster Status
- Test Cluster Performance
- Migrate
- Overview
- Migration Tools
- Migration Scenarios
- Migrate from Aurora
- Migrate MySQL of Small Datasets
- Migrate MySQL of Large Datasets
- Migrate and Merge MySQL Shards of Small Datasets
- Migrate and Merge MySQL Shards of Large Datasets
- Migrate from CSV Files
- Migrate from SQL Files
- Migrate from One TiDB Cluster to Another TiDB Cluster
- Migrate from TiDB to MySQL-compatible Databases
- Advanced Migration
- Integrate
- Overview
- Integration Scenarios
- Maintain
- Monitor and Alert
- Troubleshoot
- TiDB Troubleshooting Map
- Identify Slow Queries
- Analyze Slow Queries
- SQL Diagnostics
- Identify Expensive Queries Using Top SQL
- Identify Expensive Queries Using Logs
- Statement Summary Tables
- Troubleshoot Hotspot Issues
- Troubleshoot Increased Read and Write Latency
- Save and Restore the On-Site Information of a Cluster
- Troubleshoot Cluster Setup
- Troubleshoot High Disk I/O Usage
- Troubleshoot Lock Conflicts
- Troubleshoot TiFlash
- Troubleshoot Write Conflicts in Optimistic Transactions
- Troubleshoot Inconsistency Between Data and Indexes
- Performance Tuning
- Tuning Guide
- Configuration Tuning
- System Tuning
- Software Tuning
- SQL Tuning
- Overview
- Understanding the Query Execution Plan
- SQL Optimization Process
- Overview
- Logic Optimization
- Physical Optimization
- Prepare Execution Plan Cache
- Control Execution Plans
- Tutorials
- TiDB Tools
- Overview
- Use Cases
- Download
- TiUP
- Documentation Map
- Overview
- Terminology and Concepts
- Manage TiUP Components
- FAQ
- Troubleshooting Guide
- Command Reference
- Overview
- TiUP Commands
- TiUP Cluster Commands
- Overview
- tiup cluster audit
- tiup cluster check
- tiup cluster clean
- tiup cluster deploy
- tiup cluster destroy
- tiup cluster disable
- tiup cluster display
- tiup cluster edit-config
- tiup cluster enable
- tiup cluster help
- tiup cluster import
- tiup cluster list
- tiup cluster patch
- tiup cluster prune
- tiup cluster reload
- tiup cluster rename
- tiup cluster replay
- tiup cluster restart
- tiup cluster scale-in
- tiup cluster scale-out
- tiup cluster start
- tiup cluster stop
- tiup cluster template
- tiup cluster upgrade
- TiUP DM Commands
- Overview
- tiup dm audit
- tiup dm deploy
- tiup dm destroy
- tiup dm disable
- tiup dm display
- tiup dm edit-config
- tiup dm enable
- tiup dm help
- tiup dm import
- tiup dm list
- tiup dm patch
- tiup dm prune
- tiup dm reload
- tiup dm replay
- tiup dm restart
- tiup dm scale-in
- tiup dm scale-out
- tiup dm start
- tiup dm stop
- tiup dm template
- tiup dm upgrade
- TiDB Cluster Topology Reference
- DM Cluster Topology Reference
- Mirror Reference Guide
- TiUP Components
- PingCAP Clinic Diagnostic Service
- TiDB Operator
- Dumpling
- TiDB Lightning
- TiDB Data Migration
- About TiDB Data Migration
- Architecture
- Quick Start
- Deploy a DM cluster
- Tutorials
- Advanced Tutorials
- Maintain
- Cluster Upgrade
- Tools
- Performance Tuning
- Manage Data Sources
- Manage Tasks
- Export and Import Data Sources and Task Configurations of Clusters
- Handle Alerts
- Daily Check
- Reference
- Architecture
- Command Line
- Configuration Files
- OpenAPI
- Compatibility Catalog
- Secure
- Monitoring and Alerts
- Error Codes
- Glossary
- Example
- Troubleshoot
- Release Notes
- Backup & Restore (BR)
- Point-in-Time Recovery
- TiDB Binlog
- TiCDC
- Dumpling
- sync-diff-inspector
- TiSpark
- Reference
- Cluster Architecture
- Key Monitoring Metrics
- Secure
- Privileges
- SQL
- SQL Language Structure and Syntax
- SQL Statements
ADD COLUMNADD INDEXADMINADMIN CANCEL DDLADMIN CHECKSUM TABLEADMIN CHECK [TABLE|INDEX]ADMIN SHOW DDL [JOBS|QUERIES]ADMIN SHOW TELEMETRYALTER DATABASEALTER INDEXALTER INSTANCEALTER PLACEMENT POLICYALTER TABLEALTER TABLE COMPACTALTER TABLE SET TIFLASH MODEALTER USERANALYZE TABLEBACKUPBATCHBEGINCHANGE COLUMNCOMMITCHANGE DRAINERCHANGE PUMPCREATE [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGCREATE DATABASECREATE INDEXCREATE PLACEMENT POLICYCREATE ROLECREATE SEQUENCECREATE TABLE LIKECREATE TABLECREATE USERCREATE VIEWDEALLOCATEDELETEDESCDESCRIBEDODROP [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGDROP COLUMNDROP DATABASEDROP INDEXDROP PLACEMENT POLICYDROP ROLEDROP SEQUENCEDROP STATSDROP TABLEDROP USERDROP VIEWEXECUTEEXPLAIN ANALYZEEXPLAINFLASHBACK TABLEFLUSH PRIVILEGESFLUSH STATUSFLUSH TABLESGRANT <privileges>GRANT <role>INSERTKILL [TIDB]LOAD DATALOAD STATSMODIFY COLUMNPREPARERECOVER TABLERENAME INDEXRENAME TABLEREPLACERESTOREREVOKE <privileges>REVOKE <role>ROLLBACKSAVEPOINTSELECTSET DEFAULT ROLESET [NAMES|CHARACTER SET]SET PASSWORDSET ROLESET TRANSACTIONSET [GLOBAL|SESSION] <variable>SHOW ANALYZE STATUSSHOW [BACKUPS|RESTORES]SHOW [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGSSHOW BUILTINSSHOW CHARACTER SETSHOW COLLATIONSHOW [FULL] COLUMNS FROMSHOW CONFIGSHOW CREATE PLACEMENT POLICYSHOW CREATE SEQUENCESHOW CREATE TABLESHOW CREATE USERSHOW DATABASESSHOW DRAINER STATUSSHOW ENGINESSHOW ERRORSSHOW [FULL] FIELDS FROMSHOW GRANTSSHOW INDEX [FROM|IN]SHOW INDEXES [FROM|IN]SHOW KEYS [FROM|IN]SHOW MASTER STATUSSHOW PLACEMENTSHOW PLACEMENT FORSHOW PLACEMENT LABELSSHOW PLUGINSSHOW PRIVILEGESSHOW [FULL] PROCESSSLISTSHOW PROFILESSHOW PUMP STATUSSHOW SCHEMASSHOW STATS_HEALTHYSHOW STATS_HISTOGRAMSSHOW STATS_METASHOW STATUSSHOW TABLE NEXT_ROW_IDSHOW TABLE REGIONSSHOW TABLE STATUSSHOW [FULL] TABLESSHOW [GLOBAL|SESSION] VARIABLESSHOW WARNINGSSHUTDOWNSPLIT REGIONSTART TRANSACTIONTABLETRACETRUNCATEUPDATEUSEWITH
- Data Types
- Functions and Operators
- Overview
- Type Conversion in Expression Evaluation
- Operators
- Control Flow Functions
- String Functions
- Numeric Functions and Operators
- Date and Time Functions
- Bit Functions and Operators
- Cast Functions and Operators
- Encryption and Compression Functions
- Locking Functions
- Information Functions
- JSON Functions
- Aggregate (GROUP BY) Functions
- Window Functions
- Miscellaneous Functions
- Precision Math
- Set Operations
- List of Expressions for Pushdown
- TiDB Specific Functions
- Clustered Indexes
- Constraints
- Generated Columns
- SQL Mode
- Table Attributes
- Transactions
- Garbage Collection (GC)
- Views
- Partitioning
- Temporary Tables
- Cached Tables
- Character Set and Collation
- Placement Rules in SQL
- System Tables
mysql- INFORMATION_SCHEMA
- Overview
ANALYZE_STATUSCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_BY_HOSTCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_BY_USERCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_GLOBALCHARACTER_SETSCLUSTER_CONFIGCLUSTER_HARDWARECLUSTER_INFOCLUSTER_LOADCLUSTER_LOGCLUSTER_SYSTEMINFOCOLLATIONSCOLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITYCOLUMNSDATA_LOCK_WAITSDDL_JOBSDEADLOCKSENGINESINSPECTION_RESULTINSPECTION_RULESINSPECTION_SUMMARYKEY_COLUMN_USAGEMETRICS_SUMMARYMETRICS_TABLESPARTITIONSPLACEMENT_POLICIESPROCESSLISTREFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTSSCHEMATASEQUENCESSESSION_VARIABLESSLOW_QUERYSTATISTICSTABLESTABLE_CONSTRAINTSTABLE_STORAGE_STATSTIDB_HOT_REGIONSTIDB_HOT_REGIONS_HISTORYTIDB_INDEXESTIDB_SERVERS_INFOTIDB_TRXTIFLASH_REPLICATIKV_REGION_PEERSTIKV_REGION_STATUSTIKV_STORE_STATUSUSER_PRIVILEGESVARIABLES_INFOVIEWS
METRICS_SCHEMA
- UI
- TiDB Dashboard
- Overview
- Maintain
- Access
- Overview Page
- Cluster Info Page
- Top SQL Page
- Key Visualizer Page
- Metrics Relation Graph
- SQL Statements Analysis
- Slow Queries Page
- Cluster Diagnostics
- Monitoring Page
- Search Logs Page
- Instance Profiling
- Session Management and Configuration
- FAQ
- CLI
- Command Line Flags
- Configuration File Parameters
- System Variables
- Storage Engines
- Telemetry
- Errors Codes
- Table Filter
- Schedule Replicas by Topology Labels
- FAQs
- Release Notes
- All Releases
- Release Timeline
- TiDB Versioning
- TiDB Installation Packages
- v6.2
- v6.1
- v6.0
- v5.4
- v5.3
- v5.2
- v5.1
- v5.0
- v4.0
- v3.1
- v3.0
- v2.1
- v2.0
- v1.0
- Glossary
TiSpark User Guide
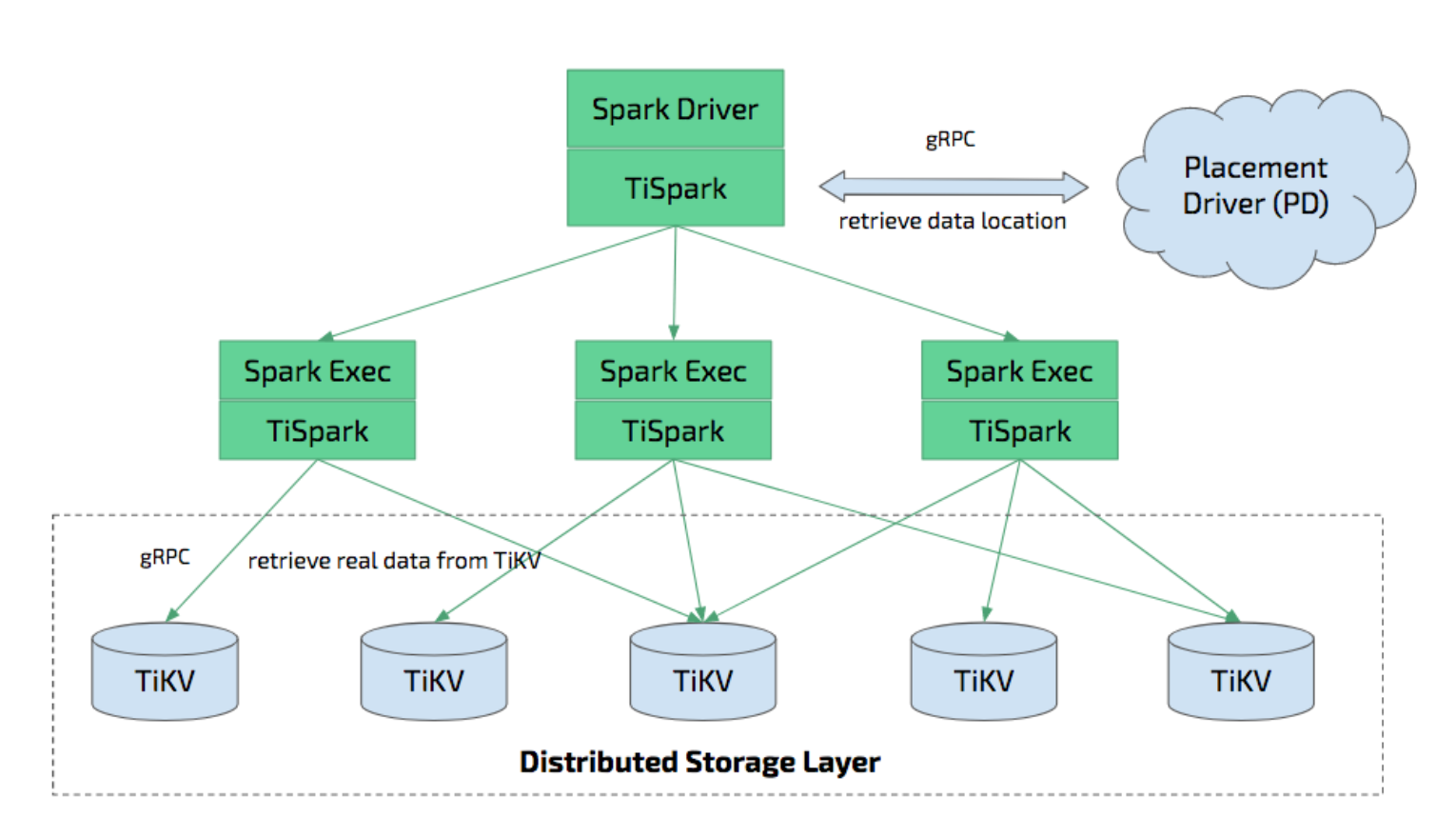
TiSpark is a thin layer built for running Apache Spark on top of TiDB/TiKV to answer the complex OLAP queries. It takes advantages of both the Spark platform and the distributed TiKV cluster and seamlessly glues to TiDB, the distributed OLTP database, to provide a Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing (HTAP) solution to serve as a one-stop solution for both online transactions and analysis.
TiFlash is another tool that enables HTAP. Both TiFlash and TiSpark allow the use of multiple hosts to execute OLAP queries on OLTP data. TiFlash stores data in a columnar format, which allows more efficient analytical queries. TiFlash and TiSpark can be used together.
TiSpark depends on the TiKV cluster and the PD cluster. You also need to set up a Spark cluster. This document provides a brief introduction to how to setup and use TiSpark. It requires some basic knowledge of Apache Spark. For more information, see Apache Spark website.
Deeply integrating with Spark Catalyst Engine, TiSpark provides precise control on computing. This allows Spark to read data from TiKV efficiently. TiSpark also supports index seek, which enables high-speed point query.
TiSpark accelerates data queries by pushing computing to TiKV so as to reduce the volume of data to be processed by Spark SQL. Meanwhile, TiSpark can use TiDB built-in statistics to select the best query plan.
With TiSpark and TiDB, you can run both transaction and analysis tasks on the same platform without building and maintaining ETLs. This simplifies the system architecture and reduces the cost of maintenance.
You can use tools of the Spark ecosystem for data processing on TiDB:
- TiSpark: Data analysis and ETLs
- TiKV: Data retrieval
- Scheduling system: Report generation
Also, TiSpark supports distributed writes to TiKV. Compared with writes to TiDB by using Spark and JDBC, distributed writes to TiKV can implement transactions (either all data are written successfully or all writes fail), and the writes are faster.
Because TiSpark accesses TiKV directly, the access control mechanisms used by TiDB Server are not applicable to TiSpark. Since TiSpark v2.5.0, TiSpark supports user authentication and authorization, for more information, see Security.
Environment setup
The following table lists the compatibility information of the supported TiSpark versions. You can choose a TiSpark version according to your need.
| TiSpark version | TiDB, TiKV, and PD versions | Spark version | Scala version |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4.x-scala_2.11 | 5.x, 4.x | 2.3.x, 2.4.x | 2.11 |
| 2.4.x-scala_2.12 | 5.x, 4.x | 2.4.x | 2.12 |
| 2.5.x | 5.x, 4.x | 3.0.x, 3.1.x | 2.12 |
| 3.0.x | 5.x, 4.x | 3.0.x, 3.1.x, 3.2.x | 2.12 |
TiSpark runs in any Spark mode such as YARN, Mesos, and Standalone.
Recommended configuration
This section describes the recommended configuration of independent deployment of TiKV and TiSpark, independent deployment of Spark and TiSpark, and co-deployed TiKV and TiSpark.
See also TiSpark Deployment Topology for more details about how to deploy TiSpark using TiUP.
Configuration of independent deployment of TiKV and TiSpark
For independent deployment of TiKV and TiSpark, it is recommended to refer to the following recommendations:
- Hardware configuration
- For general purposes, refer to the TiDB and TiKV hardware configuration recommendations.
- If the usage is more focused on the analysis scenarios, you can increase the memory of the TiKV nodes to at least 64G.
Configuration of independent deployment of Spark and TiSpark
See the Spark official website for the detail hardware recommendations. The following is a short overview of TiSpark configuration:
It is recommended to allocate 32G memory for Spark, and reserve at least 25% of the memory for the operating system and buffer cache.
It is recommended to provision at least 8 to 16 cores on per machine for Spark. Initially, you can assign all the CPU cores to Spark.
Configuration of co-deployed TiKV and TiSpark
To co-deploy TiKV and TiSpark, add TiSpark required resources to the TiKV reserved resources, and allocate 25% of the memory for the system.
Deploy the TiSpark cluster
Download TiSpark's jar package here and place it in the $SPARKPATH/jars folder.
TiSpark v2.1.x and older versions have file names that look like tispark-core-2.1.9-spark_2.4-jar-with-dependencies.jar. Please check the releases page on GitHub for the exact file name for the version you want.
The following is a short example of how to install TiSpark v2.4.1:
wget https://github.com/pingcap/tispark/releases/download/v2.4.1/tispark-assembly-2.4.1.jar
mv tispark-assembly-2.4.1.jar $SPARKPATH/jars/
Copy the spark-defaults.conf from the spark-defaults.conf.template file:
cp conf/spark-defaults.conf.template conf/spark-defaults.conf
In the spark-defaults.conf file, add the following lines:
spark.tispark.pd.addresses $pd_host:$pd_port
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.spark.sql.TiExtensions
The spark.tispark.pd.addresses configuration allows you to put in multiple PD servers. Specify the port number for each of them. For example, when you have multiple PD servers on 10.16.20.1,10.16.20.2,10.16.20.3 with the port 2379, put it as 10.16.20.1:2379,10.16.20.2:2379,10.16.20.3:2379.
If TiSpark could not communicate properly, please check your firewall configuration. You can adjust the firewall rules or disable it on your need.
Deploy TiSpark on an existing Spark cluster
Running TiSpark on an existing Spark cluster does not require a reboot of the cluster. You can use Spark's --jars parameter to introduce TiSpark as a dependency:
spark-shell --jars $TISPARK_FOLDER/tispark-${name_with_version}.jar
Deploy TiSpark without a Spark cluster
If you do not have a Spark cluster, we recommend using the standalone mode. For more information, see Spark Standalone. If you encounter any problem, see Spark official website. And you are welcome to file an issue on our GitHub.
Use Spark Shell and Spark SQL
Assume that you have successfully started the TiSpark cluster as described above. The following describes how to use Spark SQL for OLAP analysis on a table named lineitem in the tpch database.
To generate the test data via a TiDB server available on 192.168.1.101:
tiup bench tpch prepare --host 192.168.1.101 --user root
Assuming that your PD node is located at 192.168.1.100, port 2379, add the following command to $SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-defaults.conf:
spark.tispark.pd.addresses 192.168.1.100:2379
spark.sql.extensions org.apache.spark.sql.TiExtensions
Start the Spark Shell:
./bin/spark-shell
And then enter the following command in the Spark Shell as in native Apache Spark:
spark.sql("use tpch")
spark.sql("select count(*) from lineitem").show
The result is:
+-------------+
| Count (1) |
+-------------+
| 2000 |
+-------------+
Besides Spark Shell, there is also Spark SQL available. To use Spark SQL, run:
./bin/spark-sql
You can run the same query:
use tpch;
select count(*) from lineitem;
The result is:
2000
Time taken: 0.673 seconds, Fetched 1 row(s)
Use JDBC support with ThriftServer
You can use Spark Shell or Spark SQL without JDBC support. However, JDBC support is required for tools like beeline. JDBC support is provided by Thrift server. To use Spark's Thrift server, run:
./sbin/start-thriftserver.sh
To connect JDBC with Thrift server, you can use JDBC supported tools including beeline.
For example, to use it with beeline:
./bin/beeline jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
If the following message is displayed, you have enabled beeline successfully.
Beeline version 1.2.2 by Apache Hive
Then, you can run the query command:
1: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000> use testdb;
+---------+--+
| Result |
+---------+--+
+---------+--+
No rows selected (0.013 seconds)
select count(*) from account;
+-----------+--+
| count(1) |
+-----------+--+
| 1000000 |
+-----------+--+
1 row selected (1.97 seconds)
Use TiSpark together with Hive
You can use TiSpark together with Hive. Before starting Spark, you need to set the HADOOP_CONF_DIR environment variable to your Hadoop configuration folder and copy hive-site.xml to the spark/conf folder.
val tisparkDF = spark.sql("select * from tispark_table").toDF
tisparkDF.write.saveAsTable("hive_table") // save table to hive
spark.sql("select * from hive_table a, tispark_table b where a.col1 = b.col1").show // join table across Hive and Tispark
Batch write DataFrames into TiDB using TiSpark
Starting from v2.3, TiSpark natively supports batch writing DataFrames into TiDB clusters. This writing mode is implemented through the two-phase commit protocol of TiKV.
Compared with the writing through Spark + JDBC, the TiSpark batch writing has the following advantages:
| Aspects to compare | TiSpark batch writes | Spark + JDBC writes |
|---|---|---|
| Atomicity | The DataFrames either are all written successfully or all fail to write. | If the Spark task fails and exits during the writing process, a part of the data might be written successfully. |
| Isolation | During the writing process, the data being written is invisible to other transactions. | During the writing process, some successfully written data is visible to other transactions. |
| Error recovery | If the batch write fails, you only need to re-run Spark. | An application is required to achieve idempotence. For example, if the batch write fails, you need to clean up the part of the successfully written data and re-run Spark. You need to set spark.task.maxFailures=1 to prevent data duplication caused by task retry. |
| Speed | Data is directly written into TiKV, which is faster. | Data is written to TiKV through TiDB, which affects the speed. |
The following example shows how to batch write data using TiSpark via the scala API:
// select data to write
val df = spark.sql("select * from tpch.ORDERS")
// write data to tidb
df.write.
format("tidb").
option("tidb.addr", "127.0.0.1").
option("tidb.port", "4000").
option("tidb.user", "root").
option("tidb.password", "").
option("database", "tpch").
option("table", "target_orders").
mode("append").
save()
If the amount of data to write is large and the writing time exceeds ten minutes, you need to ensure that the GC time is longer than the writing time.
UPDATE mysql.tidb SET VARIABLE_VALUE="6h" WHERE VARIABLE_NAME="tikv_gc_life_time";
Refer to this document for details.
Load Spark Dataframe into TiDB using JDBC
In addition to using TiSpark to batch write DataFrames into the TiDB cluster, you can also use Spark's native JDBC support for the data writing:
import org.apache.spark.sql.execution.datasources.jdbc.JDBCOptions
val customer = spark.sql("select * from customer limit 100000")
// You might repartition the source to make it balance across nodes
// and increase the concurrency.
val df = customer.repartition(32)
df.write
.mode(saveMode = "append")
.format("jdbc")
.option("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
// Replace the host and port with that of your own and be sure to use the rewrite batch
.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:4000/test?rewriteBatchedStatements=true")
.option("useSSL", "false")
// As tested, 150 is good practice
.option(JDBCOptions.JDBC_BATCH_INSERT_SIZE, 150)
.option("dbtable", s"cust_test_select") // database name and table name here
.option("isolationLevel", "NONE") // recommended to set isolationLevel to NONE if you have a large DF to load.
.option("user", "root") // TiDB user here
.save()
It is recommended to set isolationLevel to NONE to avoid large single transactions which might potentially lead to TiDB OOM.
When you use JDBC, the default value of isolationLevel is READ_UNCOMMITTED, which causes the error of unsupported isolation level transactions. It is recommended to set the value of isolationLevel to NONE.
Statistics information
TiSpark uses TiDB statistic information for the following items:
- Determining which index to ues in your query plan with the estimated lowest cost.
- Small table broadcasting, which enables efficient broadcast join.
If you would like TiSpark to use statistic information, first you need to make sure that concerning tables have already been analyzed. Read more about how to analyze tables.
Starting from TiSpark 2.0, statistics information is default to auto load.
Security
If you are using TiSpark v2.5.0 or a later version, you can authenticate and authorize TiSpark users by using TiDB.
The authentication and authorization feature is disabled by default. To enable it, add the following configurations to the Spark configuration file spark-defaults.conf.
// Enable authentication and authorization
spark.sql.auth.enable true
// Configure TiDB information
spark.sql.tidb.addr $your_tidb_server_address
spark.sql.tidb.port $your_tidb_server_port
spark.sql.tidb.user $your_tidb_server_user
spark.sql.tidb.password $your_tidb_server_password
For more information, see Authorization and authentication through TiDB server.
After enabling the authentication and authorization feature, TiSpark Spark SQL can only use TiDB as the data source, so switching to other data sources (such as Hive) makes tables invisible.
TiSpark FAQ
Q: What are the pros/cons of independent deployment as opposed to a shared resource with an existing Spark / Hadoop cluster?
A: You can use the existing Spark cluster without a separate deployment, but if the existing cluster is busy, TiSpark will not be able to achieve the desired speed.
Q: Can I mix Spark with TiKV?
A: If TiDB and TiKV are overloaded and run critical online tasks, consider deploying TiSpark separately. You also need to consider using different NICs to ensure that OLTP's network resources are not compromised and affect online business. If the online business requirements are not high or the loading is not large enough, you can consider mixing TiSpark with TiKV deployment.
Q: What can I do if warning: WARN ObjectStore:568 - Failed to get database is returned when executing SQL statements using TiSpark?
A: You can ignore this warning. It occurs because Spark tries to load two nonexistent databases (default and global_temp) in its catalog. If you want to mute this warning, modify log4j by adding log4j.logger.org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.ObjectStore=ERROR to the log4j file in tispark/conf. You can add the parameter to the log4j file of the config under Spark. If the suffix is template, you can use the mv command to change it to properties.
Q: What can I do if java.sql.BatchUpdateException: Data Truncated is returned when executing SQL statements using TiSpark?
A: This error occurs because the length of the data written exceeds the length of the data type defined by the database. You can check the field length and adjust it accordingly.
Q: Does TiSpark read Hive metadata by default?
A: By default, TiSpark searches for the Hive database by reading the Hive metadata in hive-site. If the search task fails, it searches for the TiDB database instead, by reading the TiDB metadata.
If you do not need this default behavior, do not configure the Hive metadata in hive-site.
Q: What can I do if Error: java.io.InvalidClassException: com.pingcap.tikv.region.TiRegion; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID ... is returned when TiSpark is executing a Spark task?
A: The error message shows a serialVersionUID conflict, which occurs because you have used class and TiRegion of different versions. Because TiRegion only exists in TiSpark, multiple versions of TiSpark packages might be used. To fix this error, you need to make sure the version of TiSpark dependency is consistent among all nodes in the cluster.