- Docs Home
- About TiDB
- Quick Start
- Develop
- Overview
- Quick Start
- Build a TiDB Cluster in TiDB Cloud (Developer Tier)
- CRUD SQL in TiDB
- Build a Simple CRUD App with TiDB
- Example Applications
- Connect to TiDB
- Design Database Schema
- Write Data
- Read Data
- Transaction
- Optimize
- Troubleshoot
- Reference
- Cloud Native Development Environment
- Third-party Support
- Deploy
- Software and Hardware Requirements
- Environment Configuration Checklist
- Plan Cluster Topology
- Install and Start
- Verify Cluster Status
- Test Cluster Performance
- Migrate
- Overview
- Migration Tools
- Migration Scenarios
- Migrate from Aurora
- Migrate MySQL of Small Datasets
- Migrate MySQL of Large Datasets
- Migrate and Merge MySQL Shards of Small Datasets
- Migrate and Merge MySQL Shards of Large Datasets
- Migrate from CSV Files
- Migrate from SQL Files
- Migrate from One TiDB Cluster to Another TiDB Cluster
- Migrate from TiDB to MySQL-compatible Databases
- Advanced Migration
- Integrate
- Maintain
- Monitor and Alert
- Troubleshoot
- TiDB Troubleshooting Map
- Identify Slow Queries
- Analyze Slow Queries
- SQL Diagnostics
- Identify Expensive Queries Using Top SQL
- Identify Expensive Queries Using Logs
- Statement Summary Tables
- Troubleshoot Hotspot Issues
- Troubleshoot Increased Read and Write Latency
- Save and Restore the On-Site Information of a Cluster
- Troubleshoot Cluster Setup
- Troubleshoot High Disk I/O Usage
- Troubleshoot Lock Conflicts
- Troubleshoot TiFlash
- Troubleshoot Write Conflicts in Optimistic Transactions
- Troubleshoot Inconsistency Between Data and Indexes
- Performance Tuning
- Tuning Guide
- Configuration Tuning
- System Tuning
- Software Tuning
- SQL Tuning
- Overview
- Understanding the Query Execution Plan
- SQL Optimization Process
- Overview
- Logic Optimization
- Physical Optimization
- Prepare Execution Plan Cache
- Control Execution Plans
- Tutorials
- TiDB Tools
- Overview
- Use Cases
- Download
- TiUP
- Documentation Map
- Overview
- Terminology and Concepts
- Manage TiUP Components
- FAQ
- Troubleshooting Guide
- Command Reference
- Overview
- TiUP Commands
- TiUP Cluster Commands
- Overview
- tiup cluster audit
- tiup cluster check
- tiup cluster clean
- tiup cluster deploy
- tiup cluster destroy
- tiup cluster disable
- tiup cluster display
- tiup cluster edit-config
- tiup cluster enable
- tiup cluster help
- tiup cluster import
- tiup cluster list
- tiup cluster patch
- tiup cluster prune
- tiup cluster reload
- tiup cluster rename
- tiup cluster replay
- tiup cluster restart
- tiup cluster scale-in
- tiup cluster scale-out
- tiup cluster start
- tiup cluster stop
- tiup cluster template
- tiup cluster upgrade
- TiUP DM Commands
- Overview
- tiup dm audit
- tiup dm deploy
- tiup dm destroy
- tiup dm disable
- tiup dm display
- tiup dm edit-config
- tiup dm enable
- tiup dm help
- tiup dm import
- tiup dm list
- tiup dm patch
- tiup dm prune
- tiup dm reload
- tiup dm replay
- tiup dm restart
- tiup dm scale-in
- tiup dm scale-out
- tiup dm start
- tiup dm stop
- tiup dm template
- tiup dm upgrade
- TiDB Cluster Topology Reference
- DM Cluster Topology Reference
- Mirror Reference Guide
- TiUP Components
- PingCAP Clinic Diagnostic Service
- TiDB Operator
- Dumpling
- TiDB Lightning
- TiDB Data Migration
- About TiDB Data Migration
- Architecture
- Quick Start
- Deploy a DM cluster
- Tutorials
- Advanced Tutorials
- Maintain
- Cluster Upgrade
- Tools
- Performance Tuning
- Manage Data Sources
- Manage Tasks
- Export and Import Data Sources and Task Configurations of Clusters
- Handle Alerts
- Daily Check
- Reference
- Architecture
- Command Line
- Configuration Files
- OpenAPI
- Compatibility Catalog
- Secure
- Monitoring and Alerts
- Error Codes
- Glossary
- Example
- Troubleshoot
- Release Notes
- Backup & Restore (BR)
- TiDB Binlog
- TiCDC
- Dumpling
- sync-diff-inspector
- TiSpark
- Reference
- Cluster Architecture
- Key Monitoring Metrics
- Secure
- Privileges
- SQL
- SQL Language Structure and Syntax
- SQL Statements
ADD COLUMNADD INDEXADMINADMIN CANCEL DDLADMIN CHECKSUM TABLEADMIN CHECK [TABLE|INDEX]ADMIN SHOW DDL [JOBS|QUERIES]ADMIN SHOW TELEMETRYALTER DATABASEALTER INDEXALTER INSTANCEALTER PLACEMENT POLICYALTER TABLEALTER TABLE COMPACTALTER USERANALYZE TABLEBACKUPBATCHBEGINCHANGE COLUMNCOMMITCHANGE DRAINERCHANGE PUMPCREATE [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGCREATE DATABASECREATE INDEXCREATE PLACEMENT POLICYCREATE ROLECREATE SEQUENCECREATE TABLE LIKECREATE TABLECREATE USERCREATE VIEWDEALLOCATEDELETEDESCDESCRIBEDODROP [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGDROP COLUMNDROP DATABASEDROP INDEXDROP PLACEMENT POLICYDROP ROLEDROP SEQUENCEDROP STATSDROP TABLEDROP USERDROP VIEWEXECUTEEXPLAIN ANALYZEEXPLAINFLASHBACK TABLEFLUSH PRIVILEGESFLUSH STATUSFLUSH TABLESGRANT <privileges>GRANT <role>INSERTKILL [TIDB]LOAD DATALOAD STATSMODIFY COLUMNPREPARERECOVER TABLERENAME INDEXRENAME TABLEREPLACERESTOREREVOKE <privileges>REVOKE <role>ROLLBACKSELECTSET DEFAULT ROLESET [NAMES|CHARACTER SET]SET PASSWORDSET ROLESET TRANSACTIONSET [GLOBAL|SESSION] <variable>SHOW ANALYZE STATUSSHOW [BACKUPS|RESTORES]SHOW [GLOBAL|SESSION] BINDINGSSHOW BUILTINSSHOW CHARACTER SETSHOW COLLATIONSHOW [FULL] COLUMNS FROMSHOW CONFIGSHOW CREATE PLACEMENT POLICYSHOW CREATE SEQUENCESHOW CREATE TABLESHOW CREATE USERSHOW DATABASESSHOW DRAINER STATUSSHOW ENGINESSHOW ERRORSSHOW [FULL] FIELDS FROMSHOW GRANTSSHOW INDEX [FROM|IN]SHOW INDEXES [FROM|IN]SHOW KEYS [FROM|IN]SHOW MASTER STATUSSHOW PLACEMENTSHOW PLACEMENT FORSHOW PLACEMENT LABELSSHOW PLUGINSSHOW PRIVILEGESSHOW [FULL] PROCESSSLISTSHOW PROFILESSHOW PUMP STATUSSHOW SCHEMASSHOW STATS_HEALTHYSHOW STATS_HISTOGRAMSSHOW STATS_METASHOW STATUSSHOW TABLE NEXT_ROW_IDSHOW TABLE REGIONSSHOW TABLE STATUSSHOW [FULL] TABLESSHOW [GLOBAL|SESSION] VARIABLESSHOW WARNINGSSHUTDOWNSPLIT REGIONSTART TRANSACTIONTABLETRACETRUNCATEUPDATEUSEWITH
- Data Types
- Functions and Operators
- Overview
- Type Conversion in Expression Evaluation
- Operators
- Control Flow Functions
- String Functions
- Numeric Functions and Operators
- Date and Time Functions
- Bit Functions and Operators
- Cast Functions and Operators
- Encryption and Compression Functions
- Locking Functions
- Information Functions
- JSON Functions
- Aggregate (GROUP BY) Functions
- Window Functions
- Miscellaneous Functions
- Precision Math
- Set Operations
- List of Expressions for Pushdown
- TiDB Specific Functions
- Clustered Indexes
- Constraints
- Generated Columns
- SQL Mode
- Table Attributes
- Transactions
- Garbage Collection (GC)
- Views
- Partitioning
- Temporary Tables
- Cached Tables
- Character Set and Collation
- Placement Rules in SQL
- System Tables
mysql- INFORMATION_SCHEMA
- Overview
ANALYZE_STATUSCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_BY_HOSTCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_BY_USERCLIENT_ERRORS_SUMMARY_GLOBALCHARACTER_SETSCLUSTER_CONFIGCLUSTER_HARDWARECLUSTER_INFOCLUSTER_LOADCLUSTER_LOGCLUSTER_SYSTEMINFOCOLLATIONSCOLLATION_CHARACTER_SET_APPLICABILITYCOLUMNSDATA_LOCK_WAITSDDL_JOBSDEADLOCKSENGINESINSPECTION_RESULTINSPECTION_RULESINSPECTION_SUMMARYKEY_COLUMN_USAGEMETRICS_SUMMARYMETRICS_TABLESPARTITIONSPLACEMENT_POLICIESPROCESSLISTREFERENTIAL_CONSTRAINTSSCHEMATASEQUENCESSESSION_VARIABLESSLOW_QUERYSTATISTICSTABLESTABLE_CONSTRAINTSTABLE_STORAGE_STATSTIDB_HOT_REGIONSTIDB_HOT_REGIONS_HISTORYTIDB_INDEXESTIDB_SERVERS_INFOTIDB_TRXTIFLASH_REPLICATIKV_REGION_PEERSTIKV_REGION_STATUSTIKV_STORE_STATUSUSER_PRIVILEGESVIEWS
METRICS_SCHEMA
- UI
- TiDB Dashboard
- Overview
- Maintain
- Access
- Overview Page
- Cluster Info Page
- Top SQL Page
- Key Visualizer Page
- Metrics Relation Graph
- SQL Statements Analysis
- Slow Queries Page
- Cluster Diagnostics
- Search Logs Page
- Instance Profiling
- Session Management and Configuration
- FAQ
- CLI
- Command Line Flags
- Configuration File Parameters
- System Variables
- Storage Engines
- Telemetry
- Errors Codes
- Table Filter
- Schedule Replicas by Topology Labels
- FAQs
- Release Notes
- All Releases
- Release Timeline
- TiDB Versioning
- v6.1
- v6.0
- v5.4
- v5.3
- v5.2
- v5.1
- v5.0
- v4.0
- v3.1
- v3.0
- v2.1
- v2.0
- v1.0
- Glossary
Manage Table Schemas of Tables to be Migrated
This document describes how to manage the schema of the table in DM during migration using dmctl.
Implementation principles
When you migrate tables using DM, DM performs the following operations on the table schema:
For full export and import, DM directly exports the upstream table schema of the current time to SQL files and applies the table schema to the downstream.
For incremental replication, the whole data link contains the following table schemas, which might be the same or different:
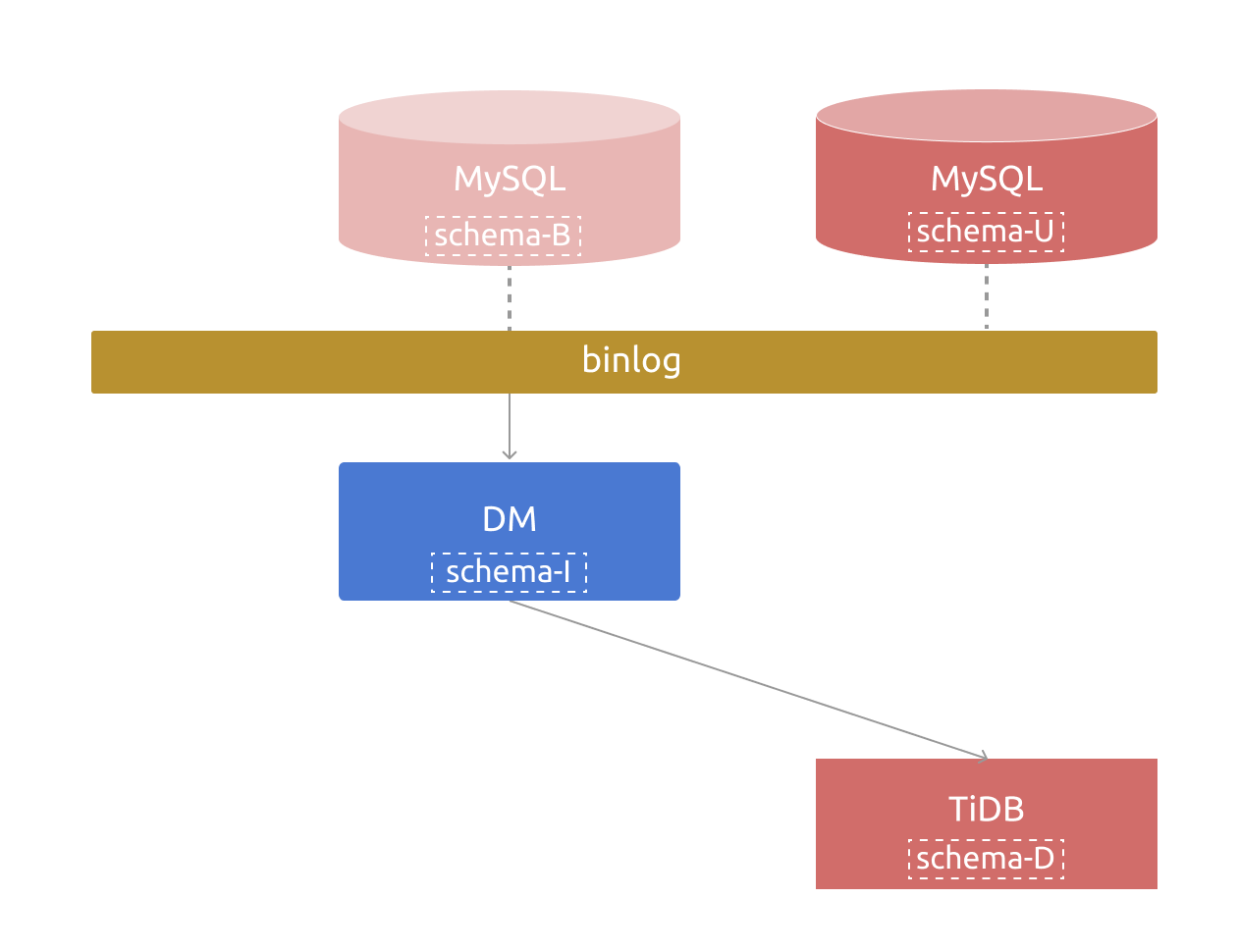
The upstream table schema at the current time, identified as
schema-U.The table schema of the binlog event currently being consumed by DM, identified as
schema-B. This schema corresponds to the upstream table schema at a historical time.The table schema currently maintained in DM (the schema tracker component), identified as
schema-I.The table schema in the downstream TiDB cluster, identified as
schema-D.In most cases, the four table schemas above are the same.
When the upstream database performs a DDL operation to change the table schema, schema-U is changed. By applying the DDL operation to the internal schema tracker component and the downstream TiDB cluster, DM updates schema-I and schema-D in an orderly manner to keep them consistent with schema-U. Therefore, DM can then normally consume the binlog event corresponding to the schema-B table schema. That is, after the DDL operation is successfully migrated, schema-U, schema-B, schema-I, and schema-D are still consistent.
However, during the migration with optimistic mode sharding DDL support enabled, the schema-D of the downstream table might be inconsistent with the schema-B and schema-I of some upstream sharded tables. In such cases, DM still keeps schema-I and schema-B consistent to ensure that the binlog event corresponding to DML can be parsed normally.
In addition, in some scenarios (such as when the downstream table has more columns than the upstream table), schema-D might be inconsistent with schema-B and schema-I.
To support the scenarios mentioned above and handle other migration interruptions caused by schema inconsistency, DM provides the binlog-schema command to obtain, modify, and delete the schema-I table schema maintained in DM.
The binlog-schema command is supported only in DM v6.0 or later versions. For earlier versions, you must use the operate-schema command.
Command
help binlog-schema
manage or show table schema in schema tracker
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema [command]
Available Commands:
delete delete table schema structure
list show table schema structure
update update tables schema structure
Flags:
-h, --help help for binlog-schema
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
Use "dmctl binlog-schema [command] --help" for more information about a command.
- Because a table schema might change during data migration, to obtain a predictable table schema, currently the
binlog-schemacommand can be used only when the data migration task is in thePausedstate. - To avoid data loss due to mishandling, it is strongly recommended to get and backup the table schema firstly before you modify the schema.
Parameters
delete: Deletes the table schema.list: Lists the table schema.update: Updates the table schema.-sor--source:- Required.
- Specifies the MySQL source that the operation is applied to.
Usage example
Get the table schema
To get the table schema, run the binlog-schema list command:
help binlog-schema list
show table schema structure
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema list <task-name> <database> <table> [flags]
Flags:
-h, --help help for list
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
If you want to get the table schema of the `db_single`.`t1` table corresponding to the mysql-replica-01 MySQL source in the db_single task, run the following command:
binlog-schema list -s mysql-replica-01 task_single db_single t1
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"sources": [
{
"result": true,
"msg": "CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `c1` int(11) NOT NULL, `c2` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`c1`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 COLLATE=latin1_bin",
"source": "mysql-replica-01",
"worker": "127.0.0.1:8262"
}
]
}
Update the table schema
To update the table schema, run the binlog-schema update command:
help binlog-schema update
update tables schema structure
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema update <task-name> <database> <table> [schema-file] [flags]
Flags:
--flush flush the table info and checkpoint immediately (default true)
--from-source use the schema from upstream database as the schema of the specified tables
--from-target use the schema from downstream database as the schema of the specified tables
-h, --help help for update
--sync sync the table info to master to resolve shard ddl lock, only for optimistic mode now (default true)
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
If you want to set the table schema of the `db_single`.`t1` table corresponding to the mysql-replica-01 MySQL source in the db_single task as follows:
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`c1` int(11) NOT NULL,
`c2` bigint(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`c1`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 COLLATE=latin1_bin
Save the CREATE TABLE statement above as a file (for example, db_single.t1-schema.sql), and run the following command:
operate-schema set -s mysql-replica-01 task_single -d db_single -t t1 db_single.t1-schema.sql
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"sources": [
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"source": "mysql-replica-01",
"worker": "127.0.0.1:8262"
}
]
}
Delete the table schema
To delete the table schema, run the binlog-schema delete command:
help binlog-schema delete
delete table schema structure
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema delete <task-name> <database> <table> [flags]
Flags:
-h, --help help for delete
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
After the table schema maintained in DM is deleted, if a DDL/DML statement related to this table needs to be migrated to the downstream, DM will try to get the table schema from the following three sources in an orderly manner:
- The
table_infofield in the checkpoint table - The meta information in the optimistic sharding DDL
- The corresponding table in the downstream TiDB
If you want to delete the table schema of the `db_single`.`t1` table corresponding to the mysql-replica-01 MySQL source in the db_single task, run the following command:
binlog-schema delete -s mysql-replica-01 task_single db_single t1
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"sources": [
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"source": "mysql-replica-01",
"worker": "127.0.0.1:8262"
}
]
}